U.C.L.A. Rheumatology Pathophysiology of Disease Course Lecture,
Second Year Medical School 1997
Rheumatoid Arthritis Page 13
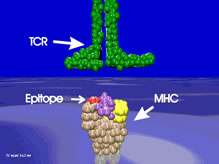
The shared epitope that promotes susceptibility to RA codes for glutamine-leucine-arginine-alanine-alanine or glutamine-arginine-arginine-alanine-alanine in the third hypervariable region of the beta chain of the Class II MHC molecule (figure 3-4). Occasionally several family members are afflicted with RA and the disease is more common among monozygotic twins of RA patients.
Despite decades of intensive study no environmental factor has been found which provokes the onset of RA. Stress, nutrition, weather changes, and pregnancy have all been associated with relapses and remissions of the disease.