U.C.L.A. Rheumatology Pathophysiology of Disease Course Lecture,
Second Year Medical School 1997
Salient Features Page 84
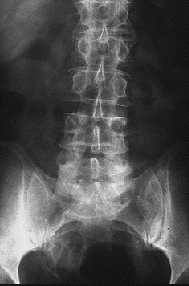
Ankylosing Spondylitis
The single most important diagnostic X-ray is erosions in the sacroiliac joint.