U.C.L.A. Rheumatology Pathophysiology of Disease Course Lecture, Second Year Medical School 2005
Systemic Lupus Erythematosus Inflammation and Immune Complex Disease Page 27
Windows Media Player
QuickTime Media Player
Real Media Player
SLE is primarily an immune complex disease. The effects of an immune complex forming on a bacteria is animated.
Animation: SLE : Immune injury in SLE is illustrated.
Animation: SLE #2: Immune Complex Deposition : SLE is primarily an immune complex disease. The effects of an immune complex forming on a bacteria is animated.
Animation: SLE : Immune injury in SLE is illustrated.
Animation: SLE #2: Immune Complex Deposition : SLE is primarily an immune complex disease. The effects of an immune complex forming on a bacteria is animated.
Animation: SLE : Immune injury in SLE is illustrated.
Animation: SLE #2: Immune Complex Deposition : SLE is primarily an immune complex disease. The effects of an immune complex forming on a bacteria is animated.
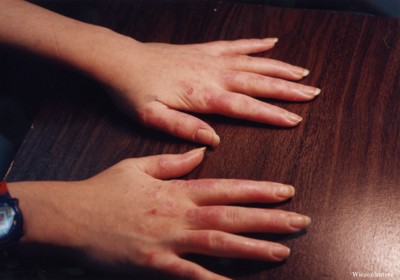
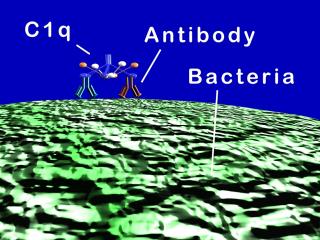
SLE is an immune complex disease. Again, in most situations, the formation of immune complexes is a good thing. The power of combining an immune complex with the destructive force of complement is shown in this cartoon.
Two antibodies have combined with the cell surface of a bacterium. The complement component, C1Q reacts with the Fc portion of the two antibody molecules, initiating the complement cascade. The inflammatory response is enhanced by the formation of small complement fragments, which will direct white cells to the site, in a process called chemotaxis. The membrane attack complex is formed, instills itself into the bacterium's membrane, leading to osmotic destruction of the cell. Here, this immune response is beneficial to the body, but imagine such destructive force directed at the human kidney, as with the patient shown above.