RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS: SLIDES & ANIMATIONS
PAGE 2
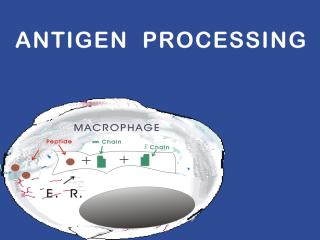
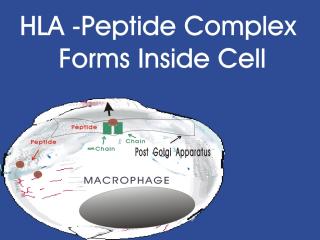
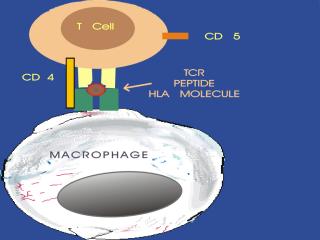
Immunity can be broken down into two broad categories, i.e. the innate or natural immunity, and specific immunity. Innate immunity is the more ancient of the two in the animal kingdom and consists of physical barriers, nonspecific phagocytosis, and macrophage derived cytokines, such as interferon and tumor necrosis factor (TNF). Specific immunity is more recently evolved and includes T-cell cellular responses and the B cells with their antibody (humoral) responses. Slides showing antigen processing by a macrophage and subsequent presentation to a T cell will be shown. Antigen is broken down into small peptides and combined with HLA (human leukocyte antigen) molecules within the cell.
Real Media Player
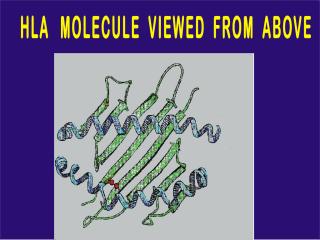
Animation 5: HLA molecule's disease causing epitope : A 3D model of the MHC Class II molecule twirls, with the disease causing epitope designated in red.
Animation 5: HLA molecule's disease causing epitope : A 3D model of theMHC Class II molecule twirls, with the disease causing epitope designated in red.
Flash Player
Animation 5: HLA molecules disease causing epitope : A 3D model of the MHC Class II molecule twirls, with the disease causing epitope designated in red.
A 3D model of the MHC Class II molecule twirls, with the disease causing epitope designated in red.
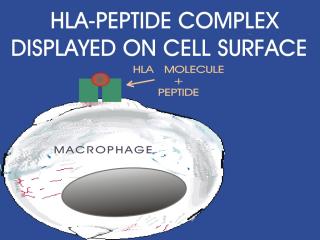
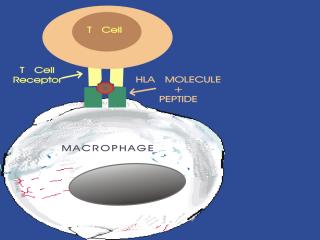
The peptide-HLA (also called peptide-MHC for major histocompatibility) complex is then displayed on the surface of the antigen presenting cell. HLA molecules play a critical role in the immune response to foreign antigens and are highly polymorphic. The MHC is the genetic cornerstone of the immune response. If a peptide cannot be bound by a HLA molecule, then there will be no immune response to it. Also, it is the HLA molecule type that predisposes to autoimmune disease.
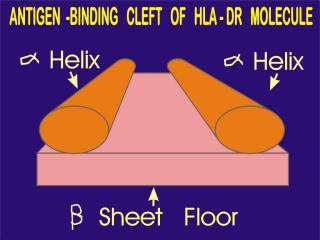
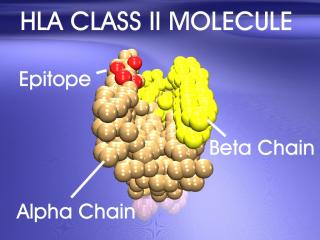
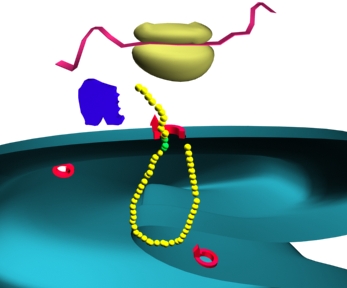
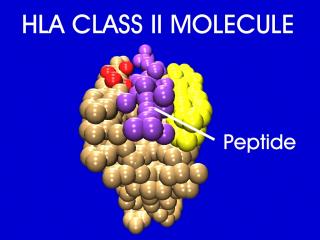
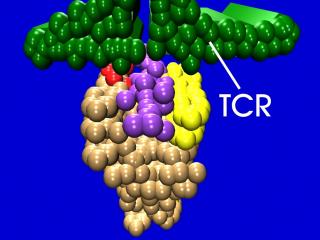
Slide 17: ""The trimolecular complex is shown."32o X 240 pixels jpeg 14kb